Mounjaro (Tirzepatide)
Mounjaro is an injectable prescription medicine used in conjunction with diet and exercise to enhance blood sugar (glucose) levels in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Mounjaro is an injectable prescription medicine used in conjunction with diet and exercise to enhance blood sugar (glucose) levels in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Wegovy (Semaglutide)
Wegovy is a once-weekly injection that you administer to yourself to aid weight loss. It contains the active substance semaglutide which mimics a natural hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) which helps reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness.
Wegovy is a once-weekly injection that you administer to yourself to aid weight loss. It contains the active substance semaglutide which mimics a natural hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) which helps reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness.
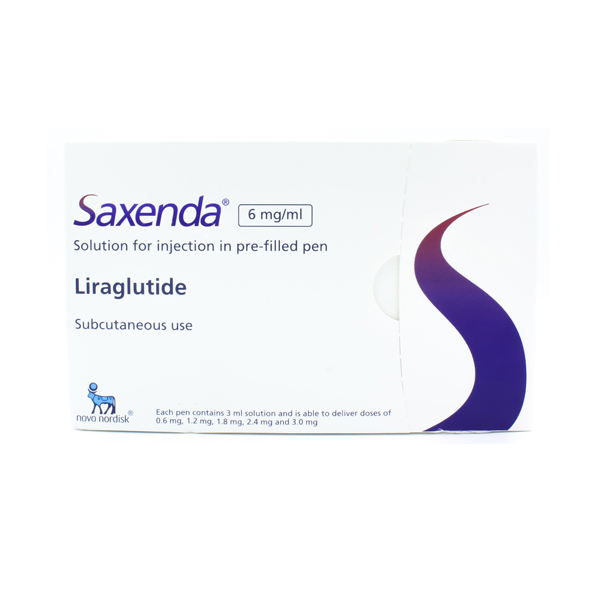
Saxenda
Saxenda is a once-daily injection that you administer to yourself to aid weight loss. It contains the active ingredient liraglutide, which is very similar to a naturally occurring hormone in your body called GLP-1. It works by making you feel less hungry, slowing down the emptying of your stomach and making you feel ‘fuller’ for longer.
Saxenda is out of stock. Nevolat, which has the same active ingredient, is available. Switch with no break in treatment
Mysimba (Naltrexone & Bupropion)
Mysimba is a prescription-only weight-loss medication containing naltrexone and bupropion. You take 1-2 tablets once or twice a day up to a maximum of 4 tablets per day. Bupropion helps to reduce your appetite so that you do not feel as hungry and are satisfied with less food. Naltrexone is thought to curb your food cravings which reduces your desire to eat.
Nevolat (generic Saxenda)
Nevolat (generic Saxenda) is a once-daily injection that you administer to yourself to aid weight loss. It contains the active ingredient liraglutide, which is very similar to a naturally occurring hormone in your body called GLP-1. It works by making you feel less hungry, slowing down the emptying of your stomach and making you feel ‘fuller’ for longer.
Orlistat (Generic Xenical)
Orlistat is a prescription-only weight-loss medication. The usual dose is one 120mg capsule taken with each of your three main meals per day. It works by reducing the absorption of fat from your diet and is very effective in weight loss when used in conjunction with exercise and a low-calorie diet.
Xenical (Orlistat)
Xenical is a prescription-only weight-loss medication containing the active ingredient orlistat. The usual dose is one 120mg capsule taken with each of your three main meals per day. It works by reducing the absorption of fat from your diet and is very effective in weight loss when used in conjunction with exercise and a low-calorie diet.
Obesity
Obesity or being very overweight is a serious health problem. In the past 20 years, the number of obese people in the UK has trebled. It is set to continue to grow at a profound rate. 1 The reasons for this huge increase are a result of the way we live, work and relax.
Generally, you develop weight problems because your calorie intake exceeds your calorie expenditure, this leads to excess energy being stored as fat.
Stress and depression may be some of the short-term effects of obesity. However, over time, obesity can lead to some very serious medical conditions, that seriously affect life expectancy and quality of life. If you believe that you are obese, you should act now and seek help if you think you need it.
The definition of obesity
Body mass index (BMI) is commonly used to calculate the ratio of a person’s height to their weight. This ratio is a quick and easy way to determine whether you are overweight or not.
If you have a BMI of 25 or more but less than 30, you are considered overweight. A BMI of over 30 is considered clinically obese.
Obesity causes and health problems
Obesity is often the result of a poor diet and lack of exercise, but it can also be affected by stress, insomnia, muscle loss, drug use and hormonal problems (such as an underactive thyroid or polycystic ovarian syndrome).
If obesity is left untreated, you may experience immediate issues such as breathlessness, insomnia, muscular pain, sweating and gallstones. You are also at risk of potentially serious long-term illnesses such as type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, high blood pressure and the risk of stroke.
How to combat obesity and control weight gain
Reducing your body weight by 10% has been proven to improve lung function, improve your breathing and have a marked reduction on joint pain, especially weight-bearing joints such as the knee If you suffer from other health issues, such as hypertension or diabetes, then losing weight will help you control these conditions better.
One of the most effective ways to combat your weight gain is to make lifestyle changes that improve your diet and increase your exercise levels. Increasing your physical activity naturally increases your metabolic rate, using calories consumed and utilising fat reserves. You should slowly increase your physical activity levels to 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on at least five days a week.
Increasing physical activity is important for weight loss. However, we understand this may be difficult for you – especially if you have mobility problems or suffer from chronic pain. Exercise should be taken up slowly and increased over many weeks, especially if you are not used to it. Walking is a great exercise and doesn’t require overexertion. Try increasing walking daily until you reach a goal of 10,000 steps daily.
Unfortunately, most people who lose weight on a calorie-controlled diet put it on again, with only 5% of obese people managing to keep their weight down. A healthy weight loss using a calorie-controlled diet is between 1-2lbs per week. This equates to a calorie deficit of 3,500 calories per week or 500 calories daily.
You should try to have a healthy and balanced diet, and be aiming to:
- Eat at least five portions of fruit and vegetables a day
- Build your meals around starchy food, choosing wholemeal and wholegrain whenever possible
- Keep high-fat dairy products to a minimum, such as cheese
- Reduce your intake of high-fat food, especially those that are high in saturated fats
- Monitor and reduce the levels of salt and sugars you consume within your diet, especially sugary soft drinks
- Keep alcohol consumption within the recommended guidelines
- Adjust your cooking methods to use less oil, such as grilling or steaming.
One of the most effective way to lose weight is to combine obesity treatment with permanent lifestyle changes, including both diet and exercise. A great way to monitor your progress is to keep a food and physical activity diary. You can track what is going well, and identify areas which require improvement, to help you achieve a healthier body weight.
Picking the right time is the key to success when it comes to weight loss. Do not choose to make a fundamental change to your lifestyle if you have already committed to other changes in your life, which may increase stress and threaten the success of your weight loss, such as moving home or starting a new job.
What are the options for obesity treatment?
If you have a BMI of over 30 you are classed as clinically obese, this increases your risk of serious health problems.
If you have already tried dieting and increasing exercise, you could request a prescription-only treatment plan prescribed by one of our doctors.
Xenical (orlistat) promotes weight loss by preventing the digestion and absorption of fat in foods. If you haven’t lost 5% of your body weight in 12 weeks, treatment should be stopped.
Saxenda (liraglutide) works by using the sugars you eat more effectively and making you feel fuller for longer. In conjunction with a calorie-controlled diet and increased levels of physical activity, you can expect to lose a minimum of 5% of your initial body weight after completing 12 weeks of treatment. If you don’t reach 5% body weight loss by 12 weeks, treatment should be stopped.
Mysimba (naltrexone/bupropion) works in two ways, by reducing cravings and by making you feel fuller for longer. The active ingredients have a well-established drug profile and work in combination to produce a weight loss effect. If you do not lose at least 5% of your body weight after 16 weeks of treatment, your doctor will evaluate if you should continue taking Mysimba.
Surgical treatments for obesity can also be considered if you have tried to modify your diet and lifestyle, and are often used as a last resort. Surgical procedures are invasive and make permanent alterations to your body to control food intake. These procedures include gastric bands, gastric bypass, biliopancreatic diversion and sleeve gastrectomy.